摘要 作者:SaritaSingh,NitinShah,JyotiMandlik,ManojNair,ShailJaggi,KalpanaKanyal摘要:本论文研究了不同精磨、抛光工艺...
作者:Sarita Singh,Nitin Shah,Jyoti Mandlik,Manoj Nair,Shail Jaggi,Kalpana Kanyal
摘要:本论文研究了不同精磨、抛光工艺对两种复合树脂材料加工的表面粗糙度影响,以及表面密封剂的使用对精磨、抛光处理后的表面粗糙度的影响。利用定制的不锈钢模具制备60个6×3mm(直径×厚度)的复合片,每30个为一组;30个为纳米填充复合材料(Z-350 3M EsPE),另外30个为微混合复合材料(Z-250 3M ESPE)。将两组试样再次随机分为3个子组并对其进行精磨、抛光加工。利用表面光度仪对所有试样的平均表面粗糙度进行测量。根据制造商的指导要求,对精磨、抛光后的试样涂上密封剂,再次进行表面粗糙度测量。利用ANOVA、配对/非配对试验对实验结果进行统计分析。实验结果表明使用纳米填充复合材料的精磨抛光系统加工出的表面比使用微混合复合材料所加工出的表面更光滑。
关键字:精磨,抛光,复合树脂材料
引言:
修复处理后的美观对于牙疾患者的心理健康影响和对身体健康的影响是等同重要的。近年来,随着人们审美的不断提高,牙医方面对修复用复合材料的需求增加。材料表面质量是决定复合材料修复处理的重要因素;而材料的表面粗糙度则影响着修复的褪色与否,并和精磨抛光加工系统以及所用的材料类型有密切关系。适当的精磨和抛光可以实现高质量的美观修复并延长修复的后续使用寿命。光滑的复合材料修复可以减少菌斑滞留、保持表面光泽并减少反复性腐烂。
新型复合材料(如微混合、纳米填充)结合了杂化复合材料和微填充复合材料的特性,有效改善了材料的机械性能,半透明度更好,表面光洁度更高。利用不同设备对复合材料进行精磨和抛光,去除树脂的氧化层,留下更加粗糙的表面。针对不同材料的恢复选取适当的表面精磨方式是非常重要的。本论文研究了不同精磨、抛光工艺对两种复合树脂材料加工的表面粗糙度影响,以及表面密封剂的使用对精磨、抛光处理后的表面粗糙度的影响。
材料和方法:
试样制备
实验所用树脂复合材料为A3品级的Z-350(纳米填充)和Z-250(微混合)。使用Denstply牌的密封剂。三种精磨抛光系统分别为Shofu精磨抛光装备、SOF-Lex复合精磨抛光装备、Mylar Strips(Unident)。用不锈钢模具制备60个光固化树脂复合材料的圆块,直径6mm深度3mm。将不锈钢模具置于玻璃调板上,待测试的复合材料嵌入每个圆块腔体内,扫去多余的复合材料。在模具上用聚酯带和载玻片密封好。利用石英-钨卤素灯从圆块两边对材料进行40秒的光固化。光源和模具中的材料之间的距离按照相关标准进行校准。最终制备出60个复合片。将所有试样放在37℃的盛有蒸馏水的培养皿中24小时。
精磨抛光实验步骤、密封剂的使用和表面粗糙度的测量
每种复合树脂的30个样品随机分成3个子组(n=10);分别用Shofu、SOF-Lex和Mylar系统对试样分别进行精磨抛光加工。使用Shofu、SOF-Lex系统进行加工的两种材料,用金刚石精修钻以旋转运动进行15秒的表面磨削,冷却液为水;以此来模拟修复材料的初始精磨。使用Mylar加工系统的材料在光固化后不再进行精磨和抛光。利用表面光度仪对所有试样的表面粗糙度进行测量。
然后,进一步研究表面密封剂对试样表面结构的影响,将Denstply牌的密封剂涂在所有精磨抛光后的试样上,再次进行表面粗糙度测量;利用ANOVA F和配对/非配对试验对得到的结果进行统计分析。
实验结果
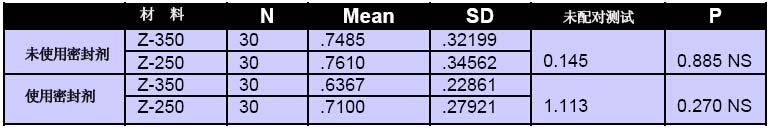
实验结果显示,Mylar组的试样表面结构最光滑,Sof-Lex系统加工出的材料比Shofu系统加工出的要好。使用密封剂后的材料表面结构得到了极大的改善。不考虑精磨抛光加工,也不考虑是否使用密封剂,纳米填充复合材料的表面粗糙度值比微混合复合材料的表面粗糙度值要低(如表1、2、3所示)。
表一:纳米填充复合材料的表面粗糙度值对比(使用三种加工系统;使用密封剂前后)
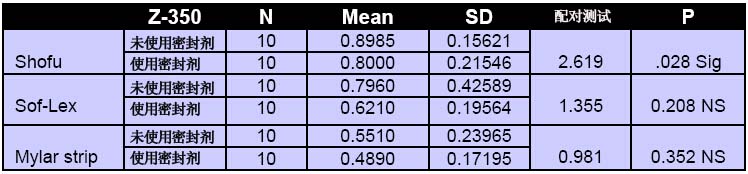
表二:微混合复合材料的表面粗糙度值对比(使用三种加工系统;使用密封剂前后)
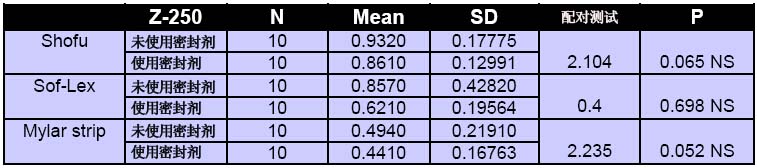
表三:材料表面粗糙度的对比
结论:
利用三种精磨抛光加工系统的两种复合材料的表面粗糙度值虽然没有统计上的显著差异,但Mylar组的表面最光滑,其次是Sof-Lex组。Shofu组的表面粗糙度值最大。微混合材料和纳米填充材料相比,纳米填充复合树脂的表面结构在三种精磨抛光加工下都较好。此外,在精磨抛光加工后,使用密封剂则显著改善了两种材料的表面结构。
参考文献
[1] Gupta R, Parkash H, Shah N, Jain V. [2005]A spectrophotometric evaluation of color changes of various tooth colored veneering materials after exposure to commonly consumed beverages. JIPS 5(2): 72−78. s
[2] Uctasli MB, Arisu HD, Omurlu H, Eliguzeloglu E, Ozcan S, Ergun G. [2007]The effect of different finishing polishing systems on the surface roughness of different composite restorative materials. J Contemp Dent Pract 1;8 (2):89−96.
[3] LS Turkun, M Turkun. [2004] The effect of one-step polishing system on the surface roughness of three esthetic resin composite materials. Operative Dentistry, 29(2):203−211.
[4] E Ruyter. [1988]Composites - characterization of composite filling materials: reactor response. Adv Dent Res 2(1):122−129.
[5] Nuray Attar. [2007] The effect of finishing polishing procedures on the surface roughness of composite resin materials. The Journal of Contemporary Practice 8( 1).
[6] Steven R Jefferies. [2007]Abrasive finishing polishing in restorative dentistry: a state-of-the-art review. Dent Clin N Am 51:379−397
[7] Reis AF, Giannini M, Lovadino JR, dos Santos Dias CT. [2002] The effect of six polishing systems on the surface roughness of two packable resin-based composites. Am J Dent 15: 193−197.
[8] Y Korkmaz, E Ozel, N Attar, G Aksoy. [2008]The influence of one-step polishing systems on the surface roughness microhardness of nanocomposites. Operative Dentistry 33(1): 44−50.
[9] AJ St- Georges, M Bolla, D Fortin. [2005]Surface finish produced on three resin composites by new polishing systems. Operative Dentistry 30(5): 593−597.
[10] AUJ Yap, JJ Ng, SH Yap, CK Teo. [2004]Surface finish of resin-modified highly viscous glass ionomer cements produced by new one-step systems. Operative Dentistry 29(1): 87−91.
[11] CYG Takeuchi, VH Orbegoso Flores, RG Palma Dibb, H Panzeri, EHG Lara, W Dinelli. [2003]Assessing the surface roughness of a posterior resin composite: Effect of surface sealing. Operative Dentistry 28(3): 283−288.
[12] M Jung, K Eichelberger J Klimek. [2007]Surface geometry of four nanofilled one composite after one-step multiple-step polishing. Operative Dentistry 32(4): 347−355.
[1] Gupta R, Parkash H, Shah N, Jain V. [2005]A spectrophotometric evaluation of color changes of various tooth colored veneering materials after exposure to commonly consumed beverages. JIPS 5(2): 72−78. s
[2] Uctasli MB, Arisu HD, Omurlu H, Eliguzeloglu E, Ozcan S, Ergun G. [2007]The effect of different finishing polishing systems on the surface roughness of different composite restorative materials. J Contemp Dent Pract 1;8 (2):89−96.
[3] LS Turkun, M Turkun. [2004] The effect of one-step polishing system on the surface roughness of three esthetic resin composite materials. Operative Dentistry, 29(2):203−211.
[4] E Ruyter. [1988]Composites - characterization of composite filling materials: reactor response. Adv Dent Res 2(1):122−129.
[5] Nuray Attar. [2007] The effect of finishing polishing procedures on the surface roughness of composite resin materials. The Journal of Contemporary Practice 8( 1).
[6] Steven R Jefferies. [2007]Abrasive finishing polishing in restorative dentistry: a state-of-the-art review. Dent Clin N Am 51:379−397
[7] Reis AF, Giannini M, Lovadino JR, dos Santos Dias CT. [2002] The effect of six polishing systems on the surface roughness of two packable resin-based composites. Am J Dent 15: 193−197.
[8] Y Korkmaz, E Ozel, N Attar, G Aksoy. [2008]The influence of one-step polishing systems on the surface roughness microhardness of nanocomposites. Operative Dentistry 33(1): 44−50.
[9] AJ St- Georges, M Bolla, D Fortin. [2005]Surface finish produced on three resin composites by new polishing systems. Operative Dentistry 30(5): 593−597.
[10] AUJ Yap, JJ Ng, SH Yap, CK Teo. [2004]Surface finish of resin-modified highly viscous glass ionomer cements produced by new one-step systems. Operative Dentistry 29(1): 87−91.
[11] CYG Takeuchi, VH Orbegoso Flores, RG Palma Dibb, H Panzeri, EHG Lara, W Dinelli. [2003]Assessing the surface roughness of a posterior resin composite: Effect of surface sealing. Operative Dentistry 28(3): 283−288.
[12] M Jung, K Eichelberger J Klimek. [2007]Surface geometry of four nanofilled one composite after one-step multiple-step polishing. Operative Dentistry 32(4): 347−355.


 手机资讯
手机资讯 官方微信
官方微信








 豫公网安备41019702003604号
豫公网安备41019702003604号